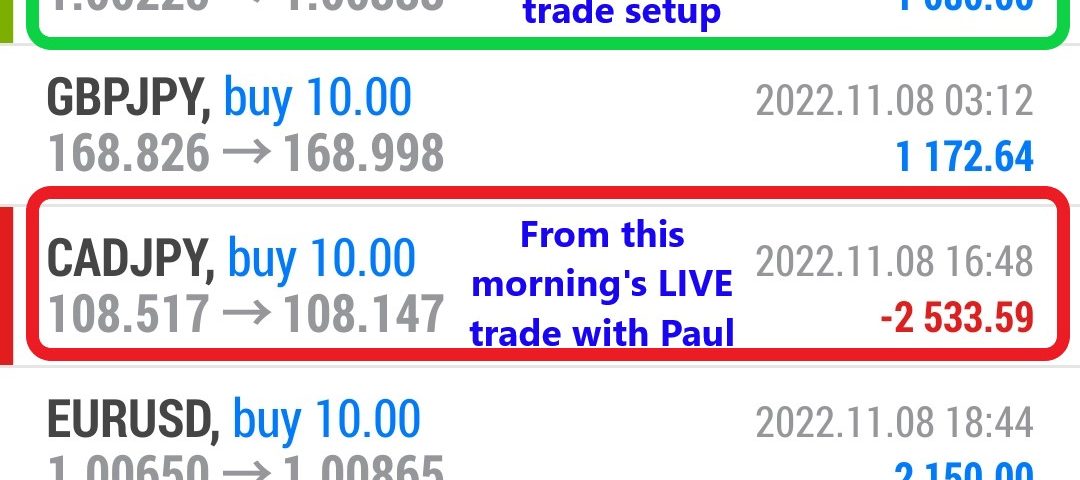
Forex Smart Trade Results November 8, 2022 – $4,760
Forex Smart Trade Results November 7, 2022 – $7,390
November 7, 2022
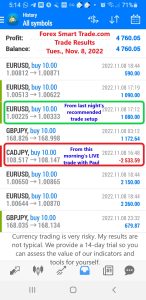
Forex Smart Trade Results November 9, 2022 – $6,486
November 9, 2022Managing Residual Risk.
Let’s look at managing residual risk from a forex broker’s perspective.
They can manage it in two ways:
- The broker can transfer this risk externally to a liquidity provider by executing a hedge trade.
- The broker can accept this risk and manage it internally.
A-Book Execution vs. Internalization + Hedge Order
Let’s see the difference between A-Book execution and Internalization followed by a hedge trade:
If the broker exercised A-Book execution, then the broker’s realized P&L vs. LP would equal:
(1.2008 − 1.2009) x 1,000,000 = -100 USD
But the broker didn’t need to A-book Elsa’s trade because Eric’s trade could’ve offset.
So if the broker had “internalized” or aggregated all GBP/USD positions, it wouldn’t need to hedge Elsa’s trade and would’ve saved money by not paying the LP’s spread.
Even after internalization, this still leaves the broker with a net short position of 2,000,000 GBP/USD.
As you can see, the broker hedged this residual risk with an LP.
Internalization
If there are enough trades of a similar size to offset one another, internalization can be very profitable for a broker.
That said, if positions remain that can’t be offset, this residual risk exposes the broker to the same market risk as a B-Book trade.
A common practice when brokers internalize trades is to:
- First, offset customer positions against each other, and then…
- Aggregate the remaining risk exposure and hedge externally with an LP based on a “volume-weighted average price” or “VWAP”.
From the example above, we can see that Elsa’s trade was internally offset by Ariel’s trade.
Elsa went long 100,000 GBP/USD, while Ariel went short 100,000 GBP/USD, so the broker’s risk exposure is zero.
But then three other traders, Eric, Jasmine, and Louis, went long GBP/USD at different prices.
With no other customers going short, the broker wants to hedge this risk.
Aggregating
Instead of hedging each trade individually, the broker aggregates the three separate trades and creates just a single hedge trade with an LP based on a VWAP of 1.2511.
Here’s how VWAP is calculated:
| TRADER | VOLUME | PRICE | NOTIONAL VALUE |
|---|---|---|---|
| Eric | 200,000 | 1.2508 | 250,160 |
| Jasmine | 300,000 | 1.2510 | 375,300 |
| Louis | 500,000 | 1.2512 | 625,600 |
| 1,000,000 | 1,251,060 |
VWAP = Total Notional Value / Total Volume VWAP = 1,251,060 / 1,000,000 VWAP = 1.2511
Aggregating multiple customer trades is a common practice for brokers since trading with most LPs requires a minimum trade size, usually at least 1 standard lot or increments of 100,000 units.
So if a broker’s customers are opening positions smaller than 100,000 units, then the broker has to wait until other customers trade where it can then “bundle” the risk from the different trades
Another reason that a broker may aggregate orders is that it reduces the time it takes to get all hedged with an LP.
STP Execution
For example, if the broker is using STP execution, the execution of many small buy orders one at a time could “signal” to an LP that this pattern may continue.
If it detects more orders interested in buying than selling, it can “shade” the price and raise the ask (buy) price higher than it normally would.
This may result in the broker’s customers getting worse fills than if the broker just sent one, single order to the LP.
This is particularly important in illiquid or fast-moving markets.
Here’s a summary of how a forex broker benefits depending on its execution method and the outcome of a trade:
| Customer’s Trade | Broker’s Order Execution | Benefit |
| WIN | B-Book (Accepts risk) | Customer’s gain is broker’s loss |
| WIN | A-Book (Transfer risk) | Broker’s spread – LP’s spread |
| WIN | Internalize (Offset risk with another customer) | Broker’s spread |
| LOSE | B-Book (Accept risk) | Customer’s loss is broker’s gain |
| LOSE | A-Book (Transfer risk) | Broker’s spread – LP’s spread |
| LOSE | Internalize (Offset risk with another customer) | Broker’s spread |
Learn to Day Trade Forex
If you’d like to earn extra income trading on the Forex market, consider learning how to currency trade with Forex Smart Trade. With their super-accurate proprietary trading tools and best-in-the-business, personalized one-on-one training, you’ll be successful. Check out the Forex Smart Trade webinar. It shows one of their trader’s trading and how easy, intuitive, and accurate the tools are. Or try the Forex Smart Trade 14-day introductory trial for just TEN dollars.